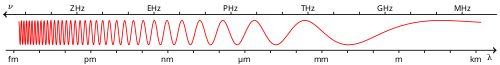
H波段 (红外)
外观

H 波段在红外天文学是指以1.65微米为中心的大气传输窗口,其半峰全宽为0.35微米[1](近红外)。
除了水蒸气的有限吸收量外,地球大气层在H波段覆盖的波长处高度半透明[2]。与其它波段相比,该窗口被红外过量污染的可能性也明显较小[3]。
该波段可用于一系列红外观测,包括太阳黑子的成像、晚型恒星的光谱研究,以及太阳系中外星涡旋或火山活动等行星现象的成像[4]。此外,恒星大气在H波段是高度透明的,窗口中的星光来自恒星大气中比其它任何波段都更深的地方。它还包括对几组谱线的访问,包括一氧化碳和氰化物[5]。
参考资料
[编辑]- ^ Ian McClean, Electronic Imaging in Astronomy, Second Edition, Springer, 2008.
- ^ Infrared Astronomy Optical Filters. www.andovercorp.com. [2023-04-08].
- ^ Hanson, M. M.; Rieke, G. H.; Luhman, K. L. Near-infrared H-band features in late O and B stars. Astronomical Journal. October 1998, 116 (4): 1915–1921. Bibcode:1998AJ....116.1915H. ISSN 0004-6256. doi:10.1086/300556
 .
.
- ^ InGaAs Cameras for Ground-Based NIR-II/SWIR Astronomy. Teledyne Princeton Instruments. [2023-04-08] (美国英语).
- ^ Wing, Robert; Jørgensen, Uffe. Stellar Spectra in the H Band. The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers. December 2003, 31 (2): 110–120. Bibcode:2003JAVSO..31..110W.
| 这是一篇与天文学相关的小作品。您可以通过编辑或修订扩充其内容。 |